Distributed Computation in TensorFlow

Distributed Computation in TensorFlow
만약 Local 컴퓨터안에 multi GPUs를 갖고 있다면, 특정 GPU를 지정해서 computation 연산을 할 수 있습니다.
Remote server에 있는 GPU를 활용하고자 할 경우, Tensorflow에서 지원하는 server를 사용하여 distributed computation처리를 할 수 있습니다.
해당 문서에서는 간단한 예제를 사용하여 방법을 알고자 합니다.
기본적으로 다음과 같은 구조를 갖고 있습니다.
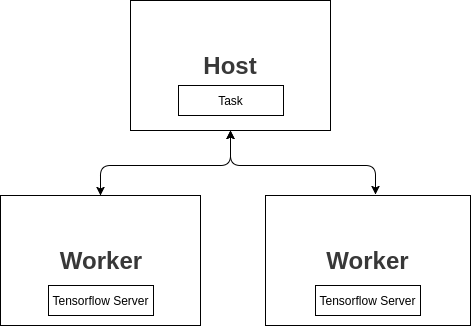
다양한 방법으로 구성을 할 수 있지만 가장 기본적인 방법은 host 그리고 worker로 나누어서 사용하는 방법입니다.
worker 는 각각의 remote server이며, 여기서는 가각 tensorflow server가 실행되면서 grpc를 통해서 host로 부터 처리할 데이터를 받습니다.
worker1 에서 처리한 내용을 worker2에서 처리할수 있으며 최종적으로 host에서 결과물을 받아서 유저에게 결과물을 보여줄 수 있습니다.
Example
Configuration
먼저 서버 정보를 JSON파일로 저장합니다.
예제에서는 worker서버 2대와 host서버 1대를 사용합니다.
config.json
{
"worker": [
"10.10.100.87:2222",
"10.10.102.74:2222"
],
"host": [
"10.10.100.87:2223"
]
}Create Worker Server
Remote 서버에서 다음의 코드를 create_server.py 로 저장합니다.
import tensorflow as tf
import argparse
import json
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--task', type=int, help='The task number')
parser.add_argument('--job', type=str, default='worker', help='job name ("worker" or "host")')
args = parser.parse_args()
cluster_spec = json.load(open('config.json', 'rt'))
cluster = tf.train.ClusterSpec(cluster_spec)
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.2, allow_growth=True)
server = tf.train.Server(cluster, job_name=args.job, task_index=args.task,
config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options))
server.start()
server.join()각각의 remote서버에서 위의 코드를 실행하되, task number를 할당해야 합니다.
task number는 config.json으로 설정한 “worker”부분의 array를 가르키는데 0에서부터 시작을 합니다.
예를 들어서 task=0 이라면 10.10.100.87:2222 가르키고, task=1이라면 10.10.102.74:2222 에서 시작을 합니다.
따라서 해당 주소가 실행하려는 서버주소와 일치해야 합니다.
$ python3.6 create_server.py --task=1
2017-10-17 14:46:22.609343: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:940] Found device 0 with properties:
name: TITAN X (Pascal)
major: 6 minor: 1 memoryClockRate (GHz) 1.531
pciBusID 0000:02:00.0
Total memory: 11.89GiB
Free memory: 10.69GiB
...Distributed Computation
import json
import tensorflow as tf
cluster_spec = json.load(open('config.json', 'rt'))
cluster = tf.train.ClusterSpec(cluster_spec)
server = tf.train.Server(cluster, job_name='host', task_index=0)
with tf.device('/job:worker/task:0'):
a = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0], shape=[2, 3], name='a')
b = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0], shape=[3, 2], name='b')
c = tf.matmul(a, b)
with tf.device('/job:worker/task:1'):
d = tf.matmul(a, b) + tf.log(100 + c)
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.1, allow_growth=True)
with tf.Session(server.target, config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)) as sess:
result = sess.run(d)
print(result)/job:worker/task:0 이부분은 worker 서버중의 첫번째인 서버에서 해당 computation을 실행시키겠다는 뜻입니다.
마찬가지로 /job:worker/task:1도 task1인 서버에서 처리를 하겠다는 뜻입니다.
궁극적으로 remote server A 그리고 remote server B에서 처리한 결과를 host서버에서 받아서 출력을 합니다.
Session초기화시에 tf.Session(server.target)을 사용하였는데 이 부분이 host 서버를 띄우는 부분입니다.