Sentiment Analysis for extracting the cause for ratings
Introduction
Spam filtering의 경우 spam 인지 또는 ham인지 예측 결과 자체가 중요합니다.
하지만 배달의 민족에서의 리뷰, 카카오T에서 택시 기사님에 대한 리뷰, Yelp 리뷰 등등은 사실 예측값이 필요하지 않습니다.
오히려 어떤 요소로 인해서 긍적정인 피드백이 나왔는지,
또는 반대로 어떤 요소로 인해서 부정적인 반응이 나왔는지 분석하는 것이 더 중요합니다.
해당 문서에서는 다음을 다룹니다.
- Kaggle Yelp Data preprocessing
- Embulk 사용하여 JSON 파일 -> MariaDB 이동 for EDA
- Sentiment Analysis
- 긍정 부정에 대한 원인 요소 찾기
Yelp Data from Kaggle
- 데이터는 Kaggle Yelp Dataset 을 사용합니다.
Yelp 데이터는 다음의 파일들로 구성이 되어 있습니다.
- yelp_academic_dataset_business.json : 상점의 rating 점수, 좌표, 도시, 리뷰 갯수 등등의 데이터
- yelp-dataset/yelp_academic_dataset_review.json : 리뷰글, rating, cool, funny, useful 등등의 점수 데이터
- yelp_academic_dataset_user.json : 유저정보 (관계망 분석시 사용가능 - 본문에서는 사용 안함)
- yelp-dataset/yelp_academic_dataset_checkin.json : checkin 에 대한 시계열 데이터 존재
- yelp-dataset/yelp_academic_dataset_tip.json : Tip 코멘트 글, like갯수 데이터
Sentiment analysis model을 만들기 위해서 사용하는 데이터는 yelp_academic_dataset_business.json 파일
그리고 yelp_academic_dataset_review.json 데이터 입니다.
Embulk to transfer data to MariaDB
Business Data (JSON -> Pandas -> CSV -> MariaDB)
preprocessing이 필요해서 business.json 파일은 pandas로 먼저 불러낸후 -> csv로 변환했습니다.
bs_data = pd.read_json('yelp_academic_dataset_business.json', lines=True)
# 숙박업체만 필터링 (category에서 hotel검색시 이상한 업체들도 나와서 이름으로 필터링)
bs_data['name'] = bs_data['name'].str.lower()
bs_data = bs_data[bs_data['name'].str.contains('hotel|motel| inn')]
# H3 추가
bs_data['h3'] = bs_data[['latitude', 'longitude']].apply(
lambda x: h3.geo_to_h3(x['latitude'], x['longitude'], 7), axis=1)
# 랭크 추가
bs_data['rank'] = bs_data['stars'] * bs_data['review_count']
# ...그외 생략
# CSV로 저장
bs_data.to_csv('business.csv', index=False) CSV -> MariaDB 로 옮기기 위해서 seed_business.yml 파일을 다음과 같이 설정합니다.
in:
type: file
path_prefix: business.csv
parser:
type: csv
out:
type: mysql
host: localhost
user: anderson
password: ""
database: yelp
table: business
mode: replaceEmbulk 실행.
embulk guess seed_business.yml -o config_business.yml
embulk preview config_business.yml
embulk run config_business.ymlReview Data (JSON -> MariaDB)
Review 데이터의 경우 전처리에 많은 시간이 들어갑니다.
MariaDB에서 필요한 내용만 뽑을수 있도록 그냥 JSON파일을 통채로 MariaDB로 올려줍니다.
in:
type: file
path_prefix: yelp_academic_dataset_review.json
parser:
type: json
columns:
- {name: review_id, type: string}
- {name: user_id, type: string}
- {name: business_id, type: string}
- {name: stars, type: double}
- {name: useful, type: double}
- {name: funny, type: double}
- {name: cool, type: double}
- {name: text, type: string}
- {name: date, type: timestamp, format: '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'}
out:
type: mysql
host: localhost
user: anderson
password: ""
database: yelp
table: review
mode: replaceembulk guess seed_review.yml -o config_review.yml
embulk preview config_review.yml
embulk run config_review.ymlPreprocessing Data for Text Classification
Stop Words
먼저 the, a, at, of 같이 중요하지 않은 단어들을 삭제시키기 위해서 NLTK의 stopwords를 다운로드 받습니다.
import nltk
from nltk import corpus
nltk.download('stopwords')
stopwords = set(corpus.stopwords.words('english'))Target Business (벨라지오)
예제로, 라스베가스에 있는 벨라지오 호텔을 사용해서 sentiment analysis model을 만듭니다.
벨라지오의 business_id=’na4Th5DrNauOv-c43QQFvA’ 이며 SQL Query를 통해서 가져옵니다.
Binary classification으로 만들어주기 위해서 1점 그리고 2점은 0으로 만들고,
3점은 제외시키고, 4, 5점은 1로 만듭니다.
class imbalance 문제가 있기 때문에 추후 데이터 전처리시 resampling이 필요합니다.
import os
import sqlalchemy
import tempfile
import hashlib
def query(sql):
base_dir = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), 'yelp')
hash_key = hashlib.sha1(sql.encode('utf-8')).hexdigest()
file_path = os.path.join(base_dir, hash_key + '.csv')
if not os.path.exists(base_dir):
os.mkdir(base_dir)
if os.path.exists(file_path):
data = pd.read_csv(file_path, index_col=0)
else:
engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine('mysql+pymysql://anderson@localhost:3306/yelp')
data = pd.read_sql(sql, con=engine)
data.to_csv(file_path)
return data
sql = '''
select cast(stars as int) as star, useful, funny, cool, lower(text) as text
from review r
where business_id = 'na4Th5DrNauOv-c43QQFvA';
'''
data = query(sql)
data.loc[(data['star'] < 3), 'star'] = 0
data.loc[(data['star'] > 3), 'star'] = 1
data = data[data['star'] != 3]영어 이외의 review 제외
리뷰중에 간혹, 프랑스어, 태국어처럼 영어권이 아닌 리뷰가 혼합이 되어 있습니다.
필터링을 위해서 langdetect를 사용해서 영어로 쓰여진 데이터만 남도록 필터링 합니다.
from langdetect import detect as langdetect
def determine_country(x):
try:
r = langdetect(x)
except:
r = None
return r
data['country'] = data['text'].apply(determine_country)
data = data[data['country'] == 'en']Text Preprocessing
Special characters 모두 삭제 시키고, 스페이스도 한개로 줄임.
Stopwords 도 제거시킴
tokenizer = RegexpTokenizer('\w+')
no_space_regex = re.compile("[.;:!?,\"()\[\]\n\-\/\d_]")
space_regex = re.compile('\s+')
def preprocess_text(t):
t = no_space_regex.sub(' ', t)
t = space_regex.sub(' ', t)
t = t.strip()
# t = tokenizer.tokenize(t)
t = t.split(' ')
t = ' '.join(filter(lambda w: w not in stopwords, t))
return t
data['text2'] = data['text'].apply(preprocess_text)
data.dropna(inplace=True)Cross Validation Dataset and Random Sampling
- data_x: 전처리된 리뷰 문장들의 리스트
- data_y: 0->Negative Rating, 1->Positive Rating
SMOTE를 적용시키려면, 텍스트 상태에서는 안되고, count vectorized 상태에서는 할 수 있음.
결국 KNN와 같은 feature space가 필요한데.. 여기서는 빠르게 적용하기 위해서 random sampling 적용함
from imblearn.over_sampling import RandomOverSampler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
np.random.seed(1510)
data_x = np.array(data['text2']).reshape(-1, 1)
data_y = np.array(data['star']).reshape(-1, 1)
# Resampling
sampler = RandomOverSampler()
data_x, data_y = sampler.fit_resample(data_x, data_y)
# Split resampled data to train data and test data
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(data_x, data_y)
train_x = train_x.reshape(-1)
test_x = test_x.reshape(-1)Model
Bernoulli Naive Bayes Model
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.naive_bayes import BernoulliNB
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report,confusion_matrix
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
pipeline = Pipeline([
('vectorization', CountVectorizer()),
('Bernoulli NB', BernoulliNB())
])
pipeline.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = pipeline.predict(test_x)
print(classification_report(test_y, pred_y))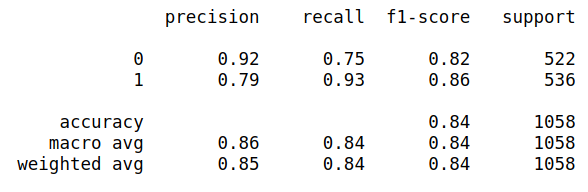
Extracting Important Words
model.feature_log_prob_을 사용해서 특정 단어에 대한 log probability를 계산할 수 있습니다.
log를 없애기 위해서 exponent를 한번 해주고, 서로의 차이를 구한뒤에 sort를 해주면
어떤 주요 단어에 의해서 negative feedback이 나왔는지 또는 positive feedback나왔는지 확인 할 수 있습니다.
vectorizer = pipeline.get_params()['vectorization']
model = pipeline.get_params()['model']
df = pd.DataFrame(model.feature_log_prob_.T,
columns=['neg', 'pos'],
index=vectorizer.get_feature_names())
df['rank'] = df.apply(lambda x: np.exp(x['neg']) - np.exp(x['pos']), axis=1)
df.sort_values('rank', inplace=True)
print('[Positive]')
print(df.iloc[:50].index)
print('\n[Negative]')
print(df.iloc[-50:].index)[Positive]
Index(['great', 'beautiful', 'amazing', 'show', 'fountain', 'fountains',
'strip', 'love', 'vegas', 'best', 'restaurants', 'always', 'casino',
'nice', 'favorite', 'view', 'conservatory', 'gorgeous', 'location',
'garden', 'wonderful', 'clean', 'pool', 'glass', 'lobby', 'loved',
'every', 'awesome', 'stayed', 'flowers', 'buffet', 'place', 'spacious',
'spa', 'friendly', 'ceiling', 'pools', 'comfortable', 'worth', 'area',
'perfect', 'everything', 'definitely', 'fun', 'shopping', 'watch',
'pretty', 'enjoyed', 'music', 'huge'],
dtype='object')
[Negative]
Index(['people', 'parking', 'since', 'experience', 'hours', 'day', 'nothing',
'next', 'finally', 'took', 'horrible', 'give', 'first', 'call', 'pay',
'way', 'booked', 'came', 'get', 'worst', 'disappointed', 'got',
'checked', 'left', 'paid', 'bad', 'went', 'charge', 'rude', 'better',
'could', 'front', 'customer', 'money', 'manager', 'another', 'check',
'minutes', 'even', 'back', 'service', 'asked', 'never', 'desk', 'would',
'room', 'called', 'said', 'us', 'told'],
dtype='object')여기서 더 나아가서, 다른 업체들에서 나오는 단어들의 비중을 따져서 unique한 단어만 뽑아볼수도 있습니다.
뭐 그런건 좀 짜치는 내용이고, 핵심은 Naive Bayes의 log probability를 사용해서 핵심 단어를 뽑아 내는 것입니다.