Basic Trigonometric in Python
최근에 코딩 테스트를 봤는데, arctan 물어보는 것이 나왔습니다.
다행히 모빌리티에서 geometry 관련 코딩을 해놓은게 있어서 코딩 테스트는..
다행히 풀었지만, 기억을 더듬더듬 했습니다. 그래서.. 다시 정리.
1. Basic Trigonometry
1.1 Degree and Radian
Python의 삼각 함수는 모두 radian을 기본값으로 사용합니다.
\[\begin{align} Radian &= Degree \times \frac{\pi}{180} \\ Degree &= Radian \times \frac{180}{\pi} \\ 2\pi Radians &= 360^o \\ \pi Radians &= 180^o \end{align}\]import math
def to_radian(degree):
return degree * math.pi / 180
def to_degree(radian):
return radian * 180 / math.pi라이러리 사용시 math 사용
> import math
>
> math.degrees(2 * math.pi) # 360
> math.radians(180) # 3.141596...1.2 Basic Trigonometry
\[\begin{align} sin\theta &= y / r \\ cos\theta &= x / r \\ tan\theta &= y / x = sin\theta / cos\theta \\ csc\theta &= 1 / sin\theta \\ sec\theta &= 1 / cos\theta \\ cat\theta &= 1 / tan\theta \\ r &= \sqrt{x^2 + y^2} \end{align}\]- y: height (높이)
- x: base (밑변)
- r: hypotenuse (빗변)
- csc: cosecant (코시컨트)
- sec: secant (시컨트)
- cot: cotangent (코탄젠트)
참고.. 중학교때 배운것들..
| \(\theta\) | \(0^\circ\) | \(30^\circ\) | \(45^\circ\) | \(60^\circ\) | \(90^\circ\) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| \(sin\theta\) | 0 | 1/2 | \(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\) | \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) | 1 |
| \(cos\theta\) | 1 | \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) | \(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\) | \(\frac{1}{2}\) | 0 |
| \(tan\theta\) | 0 | \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\) | 1 | \(\sqrt{3}\) | 0 |
| Radian | \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) | \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) | \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) | \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) |
> math.sin(30 * math.pi / 180) # 0.5
> math.cos(45 * math.pi / 180) # \sqrt(2)/2
> math.tan(60 * math.pi / 180) # \sqrt(3)좌표계를 통한 radian값 계산은 다음과 같이 합니다.
def sin(x, y):
r = math.sqrt(y ** 2 + x ** 2)
return to_radian(y / r)
def cos(x, y):
r = math.sqrt(y ** 2 + x ** 2)
return to_radian(x / r)
def tan(x, y):
return to_radian(y / x)1.3 arctangent - x, y 좌표를 알때 각도를 알고 싶을때
만약 좌표를 알고 있을때, \(\theta\) 에 해당하는 radian 값을 알고 싶을때 어떻게 계산하면 될까요?
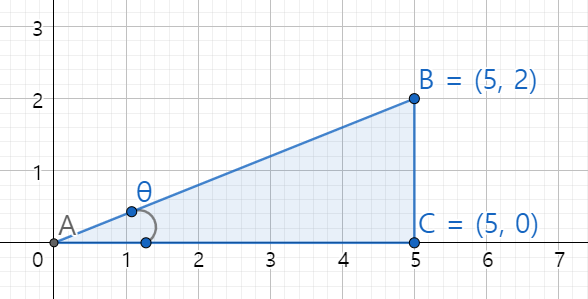
arctan 를 사용해서 각도를 계산할 수 있습니다.
arctan는 tan의 역함수이며, 수식으로는 \(tan^{-1} = arctan\) 이렇게 사용합니다.
(주의할점은 \(tan^{-1}\) 에서 -1의 의미가 역함수라는 뜻이지, -1 지수가 아닙니다. 즉 \(tan^{-1} \neq \frac{1}{tan}\) 입니다)
- 리턴값의 범위: \(-\pi\) 부터 \(\pi\) 의 radians 입니다. (즉 0 ~ 180도부터 0 ~ -180도 까지의 범위입니다.)
Python에서는 math.atan2(y, x) -> radian 을 사용합니다.
# 포인트는 atan2 의 범위는 [-pi/2, pi/2] 이기 때문에
# 180도 이상부터는 (y값이 음수) 부터는 음수의 영역대 입니다.
# 중요한 이유는 atan2 의 각도를 array와 함께 사용시 180도에서 -> -179 도로 변하게 되니..
# 범위를 찾는경우 circular array 를 사용하는 방법으로 문제를 해결해야 합니다.
> math.atan2( 0, 1) # 0
> math.atan2( 1, 1) # 0.7853 radians // 45도
> math.atan2( 1, 0) # 1.5707 radians // 90도
> math.atan2( 1, -1) # 2.3561 radians // 135도
> math.atan2( 0, -1) # 3.1415 radians // 180도
> math.atan2(-0.00000001, -1) # -3.1415 radians // -179.99999도
> math.atan2(-1, -1) # -2.3561 radians // -135도
> math.atan2(-1, 0) # -1.5707 radians // -90도
> math.atan2(-1, 1) # -0.7853 radians // -45도
> math.atan2( 0, 1) # 0
> math.atan2( 0, 0) # 01.4 내각(interior angle)을 알고 싶을때 - arcsin, acrcos, arctan
그림상에서 내각(interior angle)이란 30도 있는 부분을 말합니다.
세 변중에서 두 변의 길이를 알때 역함수를 사용하면 내각의 각도를 계산할 수 있습니다.
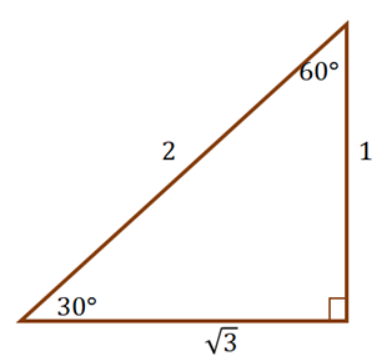
| Formula | Example | Python |
|---|---|---|
| \(\arcsin(\sin \theta) = \arcsin( y / r)\) | \(\arcsin( 1 / 2) = 30^{\circ}\) | math.degrees(math.asin(1/2)) = 30 |
| \(\arccos(\cos \theta) = \arccos( x / r)\) | \(\arccos( \sqrt(3) / 2) = 30^{\circ}\) | math.degrees(math.acos(math.sqrt(3) / 2)) = 30 |
| \(\arctan(\tan \theta) = \arctan( y / x)\) | \(\arctan( 1 / \sqrt(3) ) = 30^{\circ}\) | math.degrees(math.atan(1 / math.sqrt(3))) = 30 |
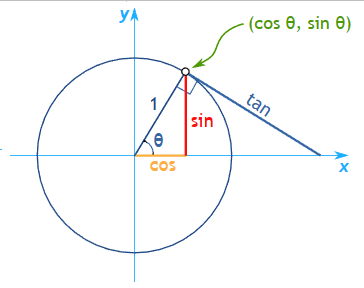
1.5 Unit Circle
- Unit Circle 에서 hypotenuse는 1이기 때문에, base(밑변)은 항상 cos이 되고 height(높이)는 항상 sin이 됩니다.
- 또한 tan = sin / cos = y/x 이며, 즉 slope 과 같다.
Law of Cosine
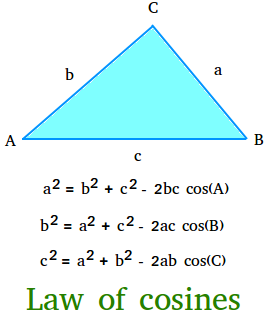
만약 C = 90 degree 라면 .. cos(90) = 0 이기 때문에 공식이 좀 달라짐.
\(\begin{align} c^2 &= a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(90) \\ &= a^2 + b^2 \end{align}\) ./