LightGBM - Handling Huge Parquet Data
1. LightGBM with huge parquet dataset
1.1 Introduction
LightGBM 아주 좋은 모델입니다.
제가 가장 최애하는 모델중의 하나입니다.
특히 latent vector 를 만들어내거나 그런 작업이 아니고, tabular dataset 을 다룬다면 더더더욱! deep learning을 쓸 필요도 없죠.
아~~ 주 좋은 모델입니다.
문제는 데이터 사이즈가 커질 때 입니다.
하둡에서 만들어진 거대한 parquets 파일들을 다루는 것부터 학습을 시키는 방법까지 해당 문서에서 다루고자 합니다.
알고 보면 매우 쉽습니다.
전체코드는 Continuous Learning Code를 참고해주세요.
1.2 Summary
batch learning 을 하게 되었을때의 인싸이트
- epoch 반드시 해야 합니다. 즉 같은 데이터를 여러번 학습 시키는 것이 꼭 필요합니다.
- epoch, num_boost_round 값이 클수록 원래 LGBMClassifier 만큼 수준으로 올라옵니다.
- 즉 LGBMClassifier 으로 학습하면 장점은 겁나 빠르고, 최적화 시키기가 매우 쉽습니다.
- batch learning 을 하게 되면, LGBMClassifier <- 이걸 쓴것보다는 결과가 더 좋게 나오기 어렵습니다. 조금 더 떨어지는 경향이 있습니다.
- 하지만 데이터 사이즈가 크면 선택 권한이 없죠.
2. Code Implementation
2.1 PrAUC
PrAUC 계산은 다음의 함수를 사용하겠습니다.
def calculate_prauc(y_true, y_prob, plot, label, method=[]):
from collections.abc import Iterable
def point_optimal_threshold(name):
# Other Metrics at the max_threshold
acc_ = accuracy_score(y_true, y_prob >= max_threshold)
f1_ = f1_score(y_true, y_prob >= max_threshold)
plot.plot(
recall[max_idx],
precision[max_idx],
marker="o",
markersize=10,
label=f"{label} | {name:5} | optimal threshold: {max_threshold}",
)
if not isinstance(method, Iterable):
method = [method]
precision, recall, thresholds = precision_recall_curve(y_true, y_prob)
auc_ = auc(recall, precision)
plot.plot(recall, precision, label=f"{label} | prauc:{auc_:.4f})")
# Optimize the thesholds
best_threshold = None
if "diff" in method:
max_idx = np.argmax(recall - precision)
max_threshold = thresholds[max_idx]
point_optimal_threshold("diff")
best_threshold = max_threshold
if "plus" in method:
max_idx = np.argmax(recall + precision)
max_threshold = thresholds[max_idx]
point_optimal_threshold("plus")
best_threshold = max_threshold
if "f1" in method:
fscores = 2 * (precision * recall) / (precision + recall)
max_idx = np.argmax(fscores)
max_threshold = thresholds[max_idx]
point_optimal_threshold("f1")
best_threshold = max_threshold
return best_threshold
2.2 LGBMClassifier
일단 continuous learning이 아닐때의 방법입니다.
# Train
model = LGBMClassifier(
metrics="prauc",
n_estimators=100,
scale_pos_weight=scale_pos_weight,
random_state=32,
)
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
예측은 다음과 같이 합니다.
# Predict
y_pred = model.predict_proba(x_test)[:, 1] >= 0.5
y_prob = model.predict_proba(x_test)[:, 1]
# Model Performance
print("scale_pos_weight:", scale_pos_weight)
print("Accuracy :", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("Precision:", precision_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("Recall :", recall_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("F1 Score :", f1_score(y_test, y_pred))
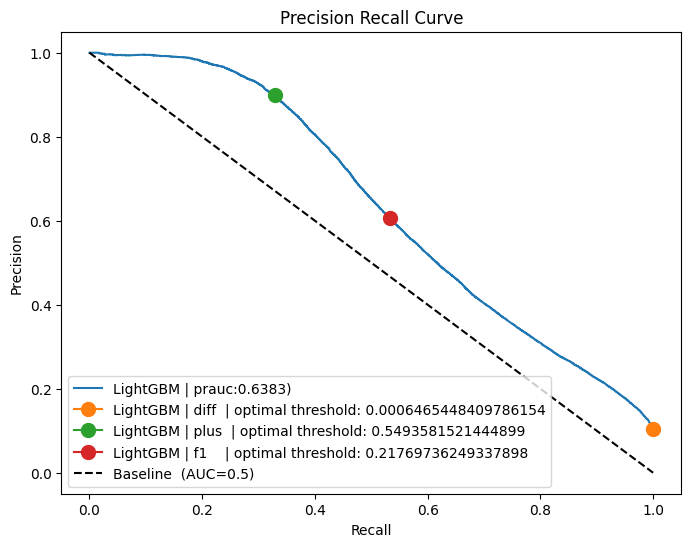
fig, plot = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(8, 6))
calculate_prauc(y_test, y_prob, plot, "LightGBM", ("diff", "plus", "f1"))
plot.plot([0, 1], [1, 0], "k--", label=f"Baseline (AUC=0.5)")
plot.set_xlabel("Recall")
plot.set_ylabel("Precision")
plot.set_title(f"Precision Recall Curve")
plot.legend(loc="lower left")
scale_pos_weight: 0.8961671428571428
Accuracy : 0.92689
Precision: 0.8745577356063042
Recall : 0.34804313738039616
F1 Score : 0.49792835069245733
2.3 Training with Huge Parquet Files
parquet 데이터는 일단 압도적으로 사이즈가 큽니다.
데이터름 모두 올려 놓는 순간 그 자체로 바로 OOM이 뜹니다.
따라서 데이터를 분할해서 학습을 시켜야 합니다.
Parquet 데이터를 다루는 코드
def iter_data(data_path) -> pd.DataFrame:
parquet_dataset = pq.ParquetDataset(data_path, use_legacy_dataset=False)
for frag in parquet_dataset.fragments:
for batch in frag.to_batches():
yield batch.to_pandas()
def split_dataset(df):
y_data = df["y"]
df.drop("y", axis=1, inplace=True)
return df, y_data
학습시키는 코드
import lightgbm as lgb
params = {
"boosting_type": "gbdt",
"objective": "binary",
"metric": "prauc",
"num_leaves": 31,
"num_iterations": 1,
"max_bin": 2000,
"num_threads": 12,
"force_col_wise": True,
"verbose": 0,
}
model = None
for epoch in tqdm(range(5), desc='epoch'):
for data in iter_data(train_path):
x_train, y_train = split_dataset(data)
scale_pos_weight = sum(y_train == 0) / len(y_train)
if model is None:
model = lgb.train(params,
lgb.Dataset(x_train, y_train),
num_boost_round=10)
else:
model = lgb.train(params,
lgb.Dataset(x_train, y_train),
num_boost_round=10,
init_model=model,
keep_training_booster=True)
저장된 모델 불러오기
model_path = 'model.txt'
model = lgb.Booster(model_file=model_path)
Evaluation
x_test = test_data.drop("y", axis=1)
y_test = test_data["y"]
# Predict
y_pred = model.predict(x_test) >= 0.5
y_prob = model.predict(x_test)
# Model Performance
print("scale_pos_weight:", scale_pos_weight)
print("Accuracy :", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("Precision:", precision_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("Recall :", recall_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("F1 Score :", f1_score(y_test, y_pred))
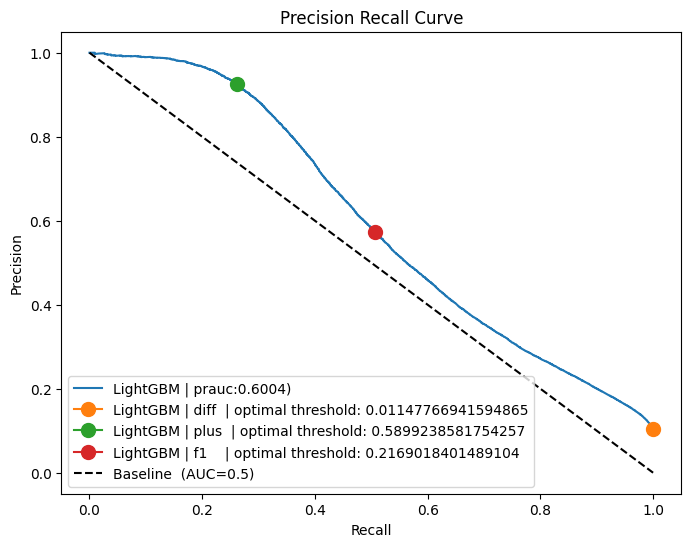
fig, plot = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(8, 6))
calculate_prauc(y_test, y_prob, plot, "LightGBM", ("diff", "plus", "f1"))
plot.plot([0, 1], [1, 0], "k--", label=f"Baseline (AUC=0.5)")
plot.set_xlabel("Recall")
plot.set_ylabel("Precision")
plot.set_title(f"Precision Recall Curve")
plot.legend(loc="lower left")
Accuracy : 0.9231666666666667
Precision: 0.8784270285239546
Recall : 0.30452174469583027
F1 Score : 0.45225987358015307
2.4 Feature Importance
- importance_type
- auto: default value
- gain: 전체 gain을 얼마나 얻었는지로 판단
- split: 몇번이나 features가 모델에서 사용되었는지로 판단
- ignore_zero: 기본값은 True이고, False 로 하게 되면 전혀 사용안된 features 들 까지도 뽑을 수 있습니다.
lgb.plot_importance(model, importance_type='gain', figsize=(7, 5), ignore_zero=False, title='gain feature importance')
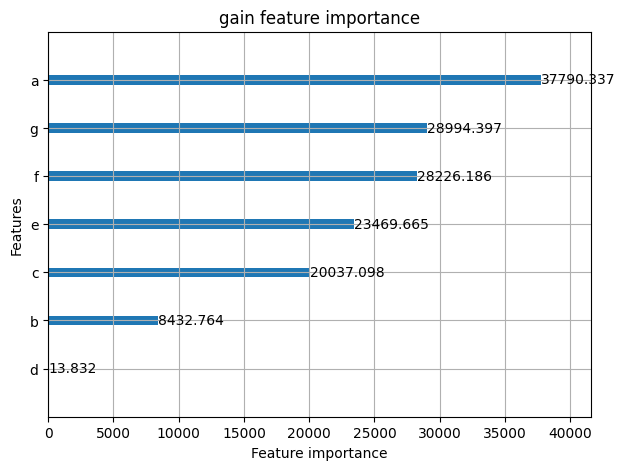
또는 따로 값을 얻으려면..
model.feature_importance(importance_type='gain')
# array([3.77903369e+04, 8.43276426e+03, 2.00370975e+04, 1.38318949e+01,
# 2.34696655e+04, 2.82261864e+04, 2.89943968e+04, 0.00000000e+00])
model.feature_name()
# ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h']